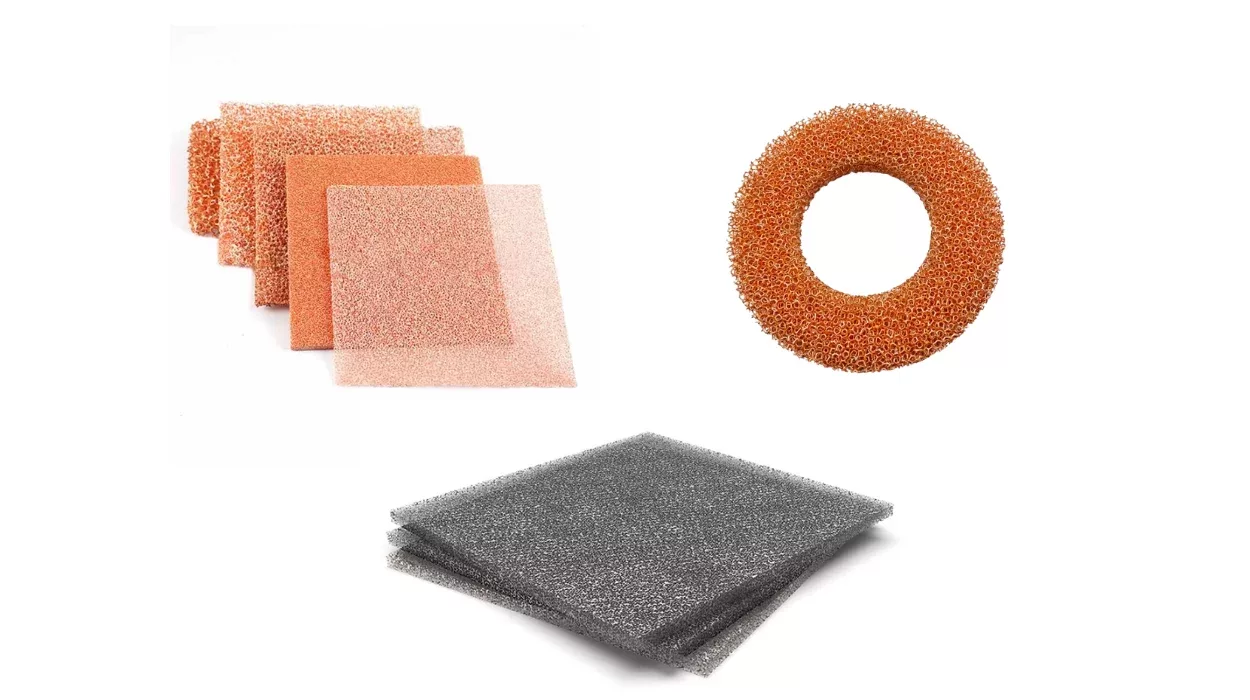
Metal foams are lightweight, strong materials with a sponge-like structure. Traditionally, they have been made using methods that mold and shape metals into this unique form. Nevertheless, with the development of 3D printing technology, it is now possible to create metal foams in a more precise and efficient way. This development has opened up new possibilities for their use in various fields.
What Are 3D-Printed Metal Foams?
3D-printed metal foams are made using 3D printers to build the foam structure layer by layer. The printers use metal powders fused using a laser or another heat source. It is helpful for creating complex shapes and patterns that were difficult to achieve with traditional methods.
Advantages of 3D Printing Metal Foams
- Precision and Customization: With 3D printing, manufacturers can design metal foams with specific shapes and sizes tailored for particular needs. This customization level helps create parts that perfectly fit applications like medical implants or specialized equipment.
- Material Efficiency: 3D printing only uses the amount of metal powder needed, reducing waste. This makes the process more efficient and cost-effective compared to traditional methods.
- Complex Structures: The technology allows for the creating of intricate internal structures within the foam, which can enhance its properties like strength and heat conductivity.
Applications of 3D-printed Metal Foams
3D-printed metal foams are used in various fields thanks to their lightweight, strong, and heat-resistant properties. Some of their critical applications include:
Aerospace Industry: In the aerospace industry, lightweight materials are essential to reduce fuel consumption and improve efficiency. 3D-printed metal foams can be used to create aircraft components that are both strong and light, helping to achieve these goals.
Biomedical Field: Metal foams are used in making implants and prosthetics because they can be designed to mimic the structure of bones. 3D printing makes it possible to create metal foams that perfectly fit a patient’s body, providing a more natural and effective solution.
Energy and Heat Management: Due to their ability to conduct heat well, 3D-printed metal foams are used in heat exchangers and cooling systems. They help transfer heat efficiently, making them valuable in electronics and power plants.
Automotive Industry: Car manufacturers are exploring 3D-printed metal foams for making lightweight vehicle parts. This improves fuel efficiency and enhances safety by using foams that can absorb impact energy in crashes.
The Future of 3D-Printed Metal Foams
The technology behind 3D-printed metal foams is still developing, and researchers are constantly finding new ways to improve it. In the future, we can expect:
- More Affordable Production: As 3D printing technology becomes more widespread, the costs of making metal foams will likely decrease, making them accessible to more industries.
- Enhanced Material Properties: Scientists are working on improving metal foams’ strength, flexibility, and conductivity by experimenting with different metals and alloys.
- Expanded Applications: With better customization and efficiency, 3D-printed metal foams could find uses in areas like architecture, environmental engineering, and even space exploration.
Conclusion
3D printing has revolutionized the way metal foams are made, offering precision, efficiency, and the ability to create complex structures. This development opens up a broad range of applications, from aerospace to medicine, and shows great promise for the future. With the development of technology, we can expect even more innovative uses for 3D-printed metal foams, making them a key material in many industries.