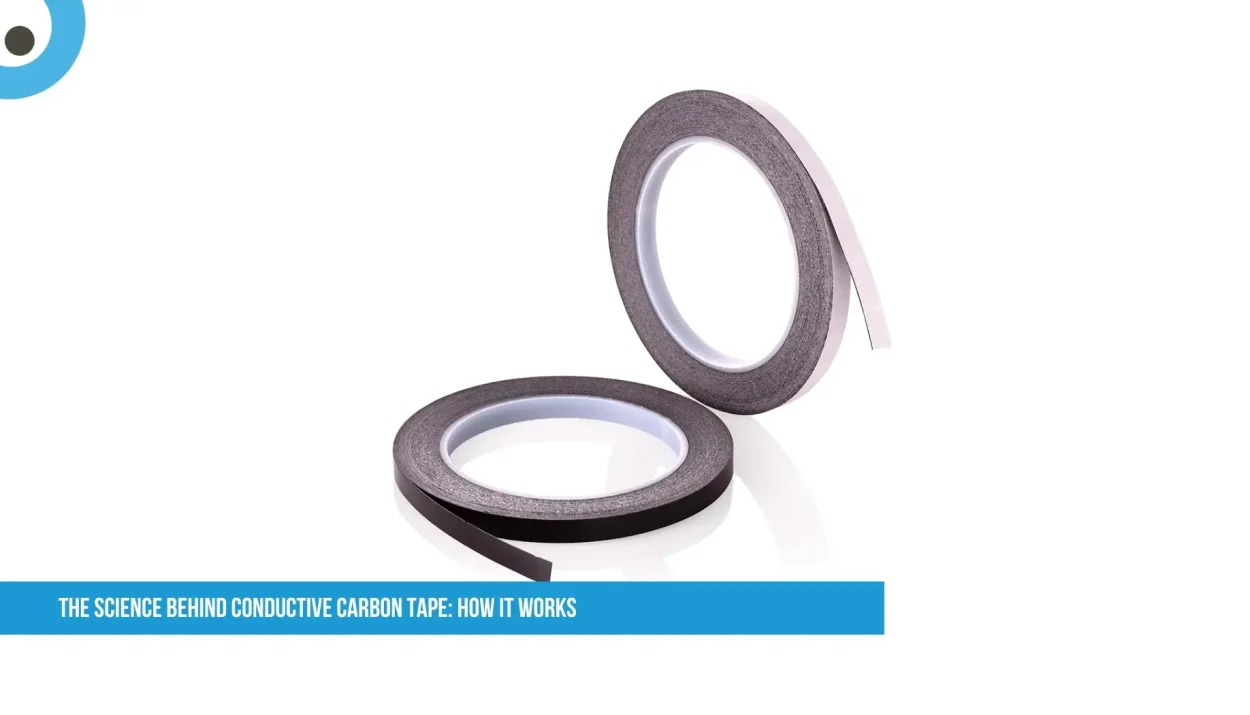
Conductive carbon tape is a handy material used in electronics, science labs, and even DIY projects. But how does it work?
What Is Conductive Carbon Tape?
Conductive carbon tape is a type of adhesive tape made with carbon particles (usually graphite or carbon black) mixed into a sticky polymer base. These carbon particles enable electricity to flow through the tape, making it electrically conductive.
Why Is Carbon Conductive?
Carbon, in forms like graphite, has free electrons that can move easily. In graphite:
Electrons are loosely held between layers of carbon atoms.
When voltage is applied, these electrons flow, creating an electric current.
Since the tape contains these carbon particles, electricity can pass through it—just like a wire, but in a flexible, sticky form.
How Does Conductive Carbon Tape Work?
Adhesion & Contact – The sticky side bonds to surfaces (like glass, plastic, or circuit boards).
Electron Flow – When connected to a power source, electrons move through the carbon particles, allowing current to pass.
Flexible Conductivity – Unlike rigid wires, the tape bends and sticks while still conducting electricity.
Where Is It Used?
Electronics Repair – Fixing broken circuits or connecting components.
Science Labs – Mounting samples in electron microscopes (SEM) because they conduct electrons well.
DIY Projects – Creating flexible circuits or wearable electronics.
Advantages Over Regular Wires
Flexible – Can bend and stick to uneven surfaces.
Lightweight – Great for small electronics.
No Soldering Needed – Easy to apply without heat.
Limitations
Not as Conductive as Metal – Higher resistance than copper wires.
Durability – Can wear out over time with bending.
Conclusion
Conductive carbon tape works due to its carbon-rich composition, which allows electrons to flow while remaining flexible and adhesive. It’s a simple yet powerful tool for electronics and science!