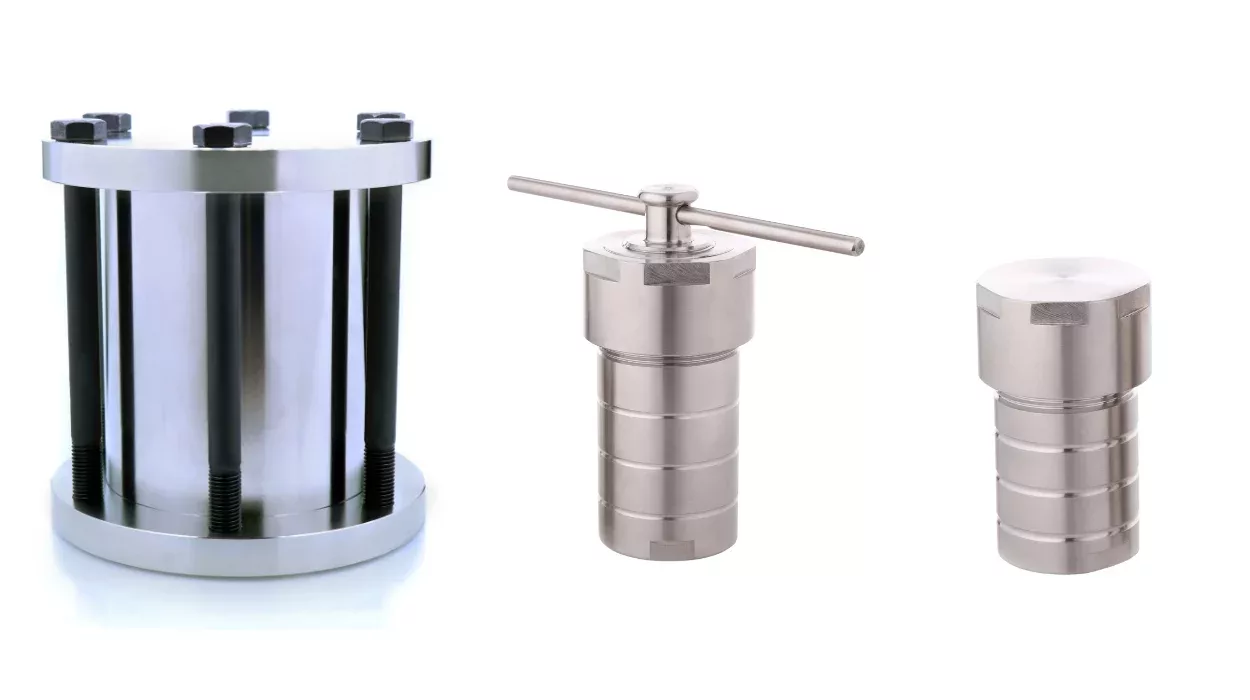
Hydrothermal autoclaves are special lab tools for conducting reactions under high temperatures and pressure. These devices play an important role in creating new materials, especially in fields like chemistry, materials science, and nanotechnology. Autoclaves can withstand extreme conditions, allowing scientists to study how materials behave or synthesize new compounds that require high heat and pressure.
There are various types of hydrothermal autoclaves, each designed for specific needs. This article will explore these different variants, discussing their unique features and uses in simple terms.
Standard Hydrothermal Autoclave
The standard hydrothermal autoclave is a basic version commonly used in labs. It has a stainless steel body and a Teflon (PTFE) liner that holds the sample. The Teflon liner is essential because it can handle high temperatures and provides a safe environment for the reaction. This type is often used for:
- Chemical reactions involving high temperatures and pressures
- Creating nanoparticles or other small materials
- Synthesizing materials that cannot be made under normal conditions
Hydrothermal Autoclave Suppliers
Key Features:
- Durable stainless steel outer body
- Teflon liner for chemical resistance
- Temperature resistance typically up to 200-250°C
This type is widely used and suitable for general-purpose research.
PPL-Lined Hydrothermal Autoclave
For reactions that require higher temperatures than the Teflon-lined autoclave can handle, there’s the PPL-lined (polyphenylene) hydrothermal autoclave. PPL is a more heat-resistant material that can work at temperatures as high as 280°C or more. This makes it ideal for researchers who must go beyond standard Teflon liners’ temperature limits.
Key Features:
- PPL liner that can withstand higher temperatures
- Stainless steel body for strength and durability
- Suitable for reactions requiring up to 280°C
The PPL-lined variant is prevalent in advanced research fields where higher temperature reactions are needed.
Reactor with Quartz Liner
Some experiments require a pure environment where even a slight contamination can ruin the results. Quartz-lined hydrothermal autoclaves are used in these cases. Quartz is a pure and chemically inert material that doesn’t react with most chemicals. However, these autoclaves can be fragile, so they must be handled carefully.
Key Features:
- Quartz liner for ultra-clean and inert conditions
- Typically more fragile and requires careful handling
- Used in high-purity reactions and synthesis
Researchers in fields like material science or those working on sensitive nanomaterials often prefer quartz-lined autoclaves.
Large-Capacity Hydrothermal Autoclave
Standard autoclaves usually have a small capacity ranging from 25 mL to 200 mL. However, specific experiments require more material or involve scaling up reactions. Large-capacity hydrothermal autoclaves can hold up to several liters of solution, allowing researchers to conduct more extensive experiments.
Key Features:
- More extensive volume options, up to several liters
- Often have reinforced construction for safety at high volumes
- Applicable for industrial applications or large-scale synthesis
These autoclaves are primarily used in industries or more extensive labs where large-scale production of materials is required.
Stirred Hydrothermal Autoclave
Some chemical reactions benefit from constant stirring because it helps materials mix better and speeds up the reaction. Stirred hydrothermal autoclaves have a built-in stirring mechanism, which keeps the solution in motion throughout the process. This ensures a more even reaction, which is especially important in chemical synthesis.
Key Features:
- Built-in stirring mechanism
- Ideal for reactions that require uniform mixing
- Helps improve the efficiency and consistency of reactions
Stirred autoclaves are widely used in research and industry to create complex compounds where even mixing is essential.
Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Autoclave
A newer type of autoclave, the microwave-assisted hydrothermal autoclave, uses microwaves to heat the sample. This can speed up reactions significantly, making it a time-saving option. Microwave-assisted autoclaves are particularly useful for creating nanomaterials and other advanced materials that require quick heating and cooling.
Key Features:
- It uses microwave energy to heat samples quickly
- Faster reaction times compared to traditional heating
- Useful in nanotechnology and materials research
This variant is ideal for labs focused on rapid synthesis or those looking to speed up their experimental processes.
Customized Hydrothermal Autoclave
Sometimes, a standard autoclave won’t meet the unique needs of a specific experiment. Customized hydrothermal autoclaves can be designed to meet these requirements. These autoclaves can have specialized linings, different heating methods, or unique shapes and sizes. Labs working on innovative materials or new technologies often use custom autoclaves tailored to their research needs.
Key Features:
- Custom-designed to meet specific research needs
- It may have unique linings, sizes, or heating options
- Ideal for highly specialized or experimental work
Conclusion
Hydrothermal autoclaves are vital tools enabling scientists to conduct impossible experiments under normal conditions. Each type serves a unique purpose, from standard autoclaves for routine lab work to specialized variants like quartz-lined or microwave-assisted autoclaves. The variety allows researchers and industries to choose suitable autoclaves based on their specific needs, whether they require higher temperatures, faster reactions, or larger volumes.
As technology advances, hydrothermal autoclaves play a central role in innovation, helping us discover new materials, improve processes, and explore the possibilities of high-temperature and high-pressure reactions.