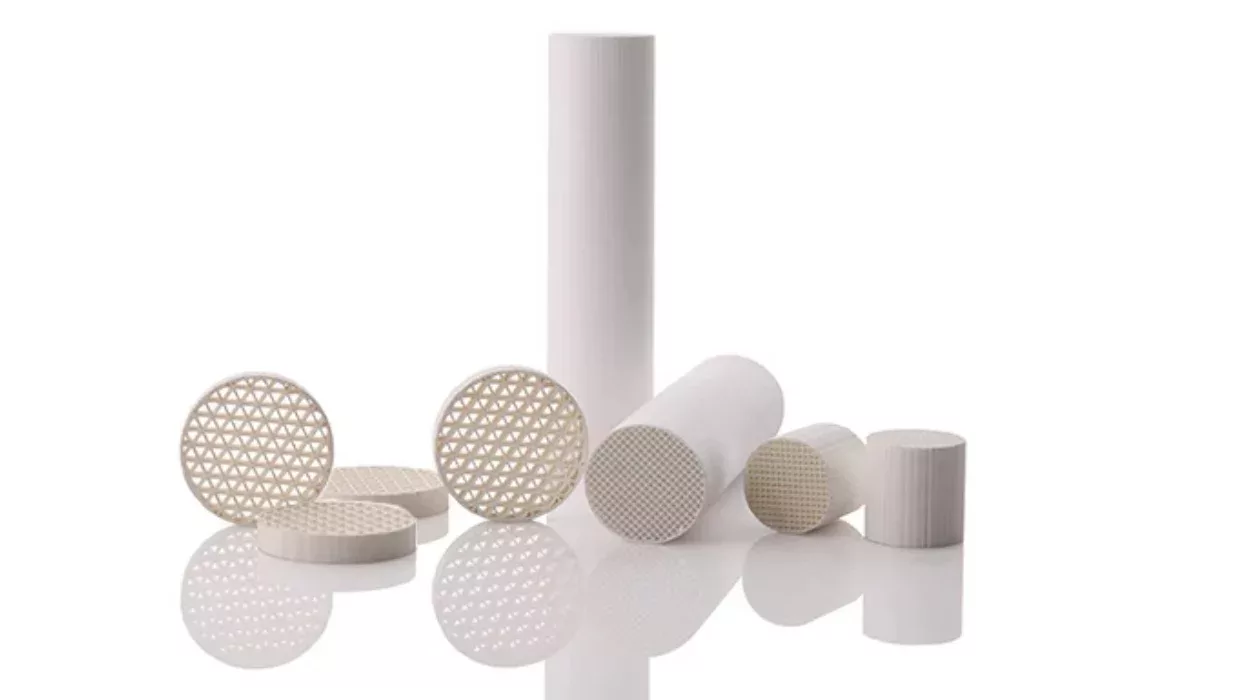
With their unique honeycomb-like structure, ceramic honeycomb substrates boast a large surface area, lightweight nature, and robust strength. These exceptional properties make them versatile for various scientific and industrial applications. Let’s straightforwardly delve into their uses.
What are Ceramic Honeycomb Substrates?
Ceramic honeycomb substrates are made from ceramic materials formed into a honeycomb-like structure. This structure consists of many small, hollow cells that create a lot of surface area relative to the volume of the material. The main characteristics of ceramic honeycomb substrates include:
- High Surface Area: The honeycomb structure provides a large surface area for reactions or filtration.
- Heat Resistance: Ceramics can withstand high temperatures without melting or breaking down.
- Chemical Resistance: They are stable and resistant to many chemicals, making them durable in harsh environments.
Ceramic Honeycomb Manufacturers
Scientific Uses of Ceramic Honeycomb Substrates
1. Catalytic Converters in Automobiles:
- Emission Control: Ceramic honeycomb substrates are vital in catalytic converters of car exhaust systems to reduce harmful emissions. The large surface area of the honeycomb structure allows for the efficient conversion of toxic gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides into slightly harmful substances like carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
2. Air and Gas Filtration:
- Pollution Control: These substrates are used in industrial filters to remove pollutants from air and gas streams. They can capture particulate matter and facilitate chemical reactions that neutralize harmful substances.
- VOC Removal: They are used to remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from industrial exhaust gases, helping to reduce air pollution.
3. Heat Exchangers:
- Energy Efficiency: Ceramic honeycomb substrates are used in heat exchangers to improve energy efficiency. Their structure allows for efficient heat transfer between different fluids or gases, which can help in processes like waste heat recovery.
4. Chemical Reactors:
- Catalysis: In chemical reactors, ceramic honeycomb substrates support catalysts. The large surface area allows for more active sites where chemical reactions can occur, improving the efficiency of processes like chemical synthesis and fuel processing.
5. Environmental Protection:
- Desulfurization: They are used in flue gas desulfurization systems to remove (SO2) from the exhaust gases of power plants and industrial facilities, helping to reduce acid rain.
- Water Purification: Ceramic honeycomb substrates are also used to remove contaminants and improve water quality through water treatment processes .
6. Laboratory Applications:
- Analytical Chemistry: In laboratory settings, these substrates are used in analytical instruments like gas chromatographs and mass spectrometers to enhance the efficiency of chemical analyses.
- Experimental Studies: Researchers use them in various experimental setups to study catalytic reactions and other chemical processes.
Conclusion
Ceramic honeycomb substrates are versatile materials with various scientific and industrial uses. Their unique honeycomb structure provides a large surface area, high heat resistance, and excellent chemical stability. These properties make them ideal for applications in catalytic converters, air and gas filtration, heat exchangers, chemical reactors, environmental protection, and laboratory research. Using ceramic honeycomb substrates, scientists and engineers can develop more efficient and environmentally friendly technologies, contributing to advancements in many fields.