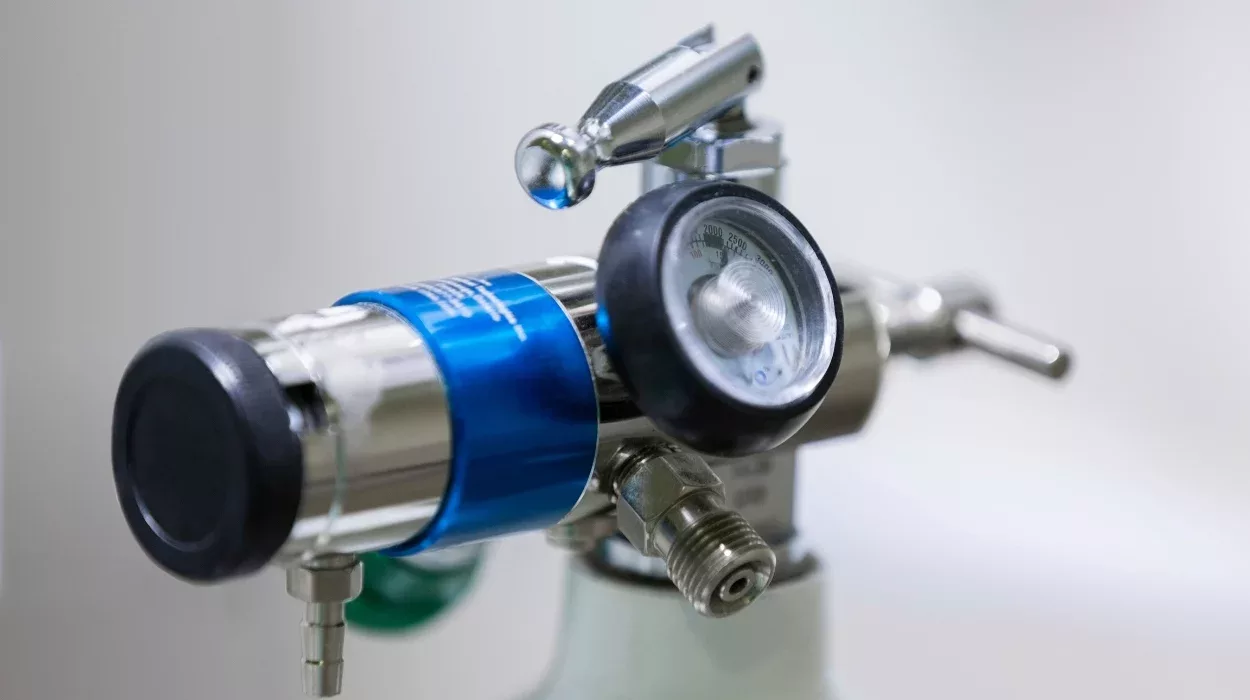
A high-pressure regulator controls and reduces the pressure of gases or liquids from a high-pressure source to a safe and usable level. In many situations, gas or liquid is stored at very high pressure in tanks or pipelines. If released at this pressure, it could be too powerful, posing risks to equipment and people. The high-pressure regulator helps to manage this pressure, allowing the gas or liquid to flow smoothly at a controlled level.
How Does a High-Pressure Regulator Work?
Inside a high-pressure regulator, there are key components that work together to adjust and maintain the desired output pressure:
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: These are the points where the gas or liquid enters and exits the regulator.
- Valve and Seat: The valve controls the flow, and the seat is the surface where the valve rests when it’s closed. Together, they determine how much pressure is allowed to pass through.
- Diaphragm: A flexible membrane that senses pressure changes. When pressure rises, the diaphragm moves to adjust the valve, maintaining the set output pressure.
- Spring Mechanism: Attached to the diaphragm, the spring helps control how much the valve opens or closes based on the desired pressure setting.
The spring and diaphragm adjust the valve opening when the regulator is set. This allows the correct amount of gas or liquid to pass through, keeping the output pressure steady even if the input pressure varies.
Why Use a High-Pressure Regulator?
A high-pressure regulator is essential for safety, equipment performance, and cost savings. Here’s why:
- Safety: High-pressure gases and liquids can be dangerous. If released without control, they could cause explosions, equipment damage, or harm to people. The regulator ensures the pressure stays within safe limits.
- Equipment Protection: Many machines and devices can only handle certain pressure levels. High-pressure regulators protect this equipment from pressure surges or fluctuations that could cause breakdowns.
- Efficiency and Cost Savings: By controlling the pressure, a regulator ensures that only the needed amount of gas or liquid is used, reducing waste and saving costs over time.
Types of High-Pressure Regulators
High-pressure regulators are available in various types to suit different applications. Some common types include:
- Single-Stage Regulator: Reduces pressure in one step from high to low. These are often used in applications where slight fluctuations in output pressure are acceptable.
- Dual-Stage Regulator: Lowers pressure in two steps for more precise control. The first stage reduces the pressure partially, and the second stage fine-tunes it to the desired level. This is ideal for applications where very stable pressure is needed.
- Adjustable and Fixed Regulators: Adjustable regulators allow users to set the desired output pressure, while fixed regulators maintain a constant output pressure without adjustments.
- Back Pressure Regulators: These work opposite to regular pressure regulators. Instead of controlling the output pressure, they maintain the pressure on the input side to ensure a steady flow.
Where are High-Pressure Regulators Used?
High-pressure regulators are used in a wide range of industries and applications:
- Industrial Manufacturing: In processes like welding, cutting, and heating, high-pressure gases are used. Regulators ensure that the pressure is suitable for each job.
- Laboratories and Research: Lab experiments and lab processes often require precise pressure control, especially when working with delicate instruments or reactions.
- Medical Applications: Oxygen and other gases used in hospitals or for medical treatments are stored in high-pressure cylinders. Regulators make sure that the gas is delivered at safe levels for patient care.
- Food and Beverage Industry: High-pressure CO₂ gas carbonates drinks in carbonated beverage systems. Regulators control the CO₂ pressure to keep it safe and consistent.
- Energy Sector: In gas distribution, regulators manage the pressure in pipelines to ensure efficient and safe delivery to different facilities.
Setting Up and Using a High-Pressure Regulator
When setting up a high-pressure regulator, follow these simple steps to ensure safe and efficient use:
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the regulator is suitable for the type of gas or liquid and the pressure range needed.
- Inspect the Regulator: Inspect the regulator for any signs of wear or damage before installation. Regular maintenance is critical to long-term safety.
- Adjust the Pressure Setting: Use the adjustment knob or dial on the regulator to set the desired output pressure. Initiate with a lower setting and gradually increase as needed.
- Test the Flow: After adjusting, open the valve slowly and monitor the output. Ensure the pressure stays steady and that there are no leaks.
Safety Tips When Using High-Pressure Regulators
High-pressure systems can be hazardous if not handled properly. Here are some safety guidelines:
- Always Turn Off When Not in Use: Turn off the gas or liquid supply when not using the regulator to prevent leaks or accidental release.
- Regular Maintenance: Check the regulator, hoses, and connections regularly for signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn-out parts.
- Avoid over-tightening: While securing connections is important, over-tightening can damage the regulator or cause leaks.
- Wear Safety Gear: Use goggles and gloves to protect against accidents when working with high-pressure systems.
Conclusion
A high-pressure regulator is critical for managing high-pressure gases and liquids safely and efficiently. By controlling the pressure, it ensures that equipment runs smoothly and that people remain safe. Whether in industrial settings, laboratories, or medical facilities, using a high-pressure regulator helps to make high-pressure systems practical and secure.