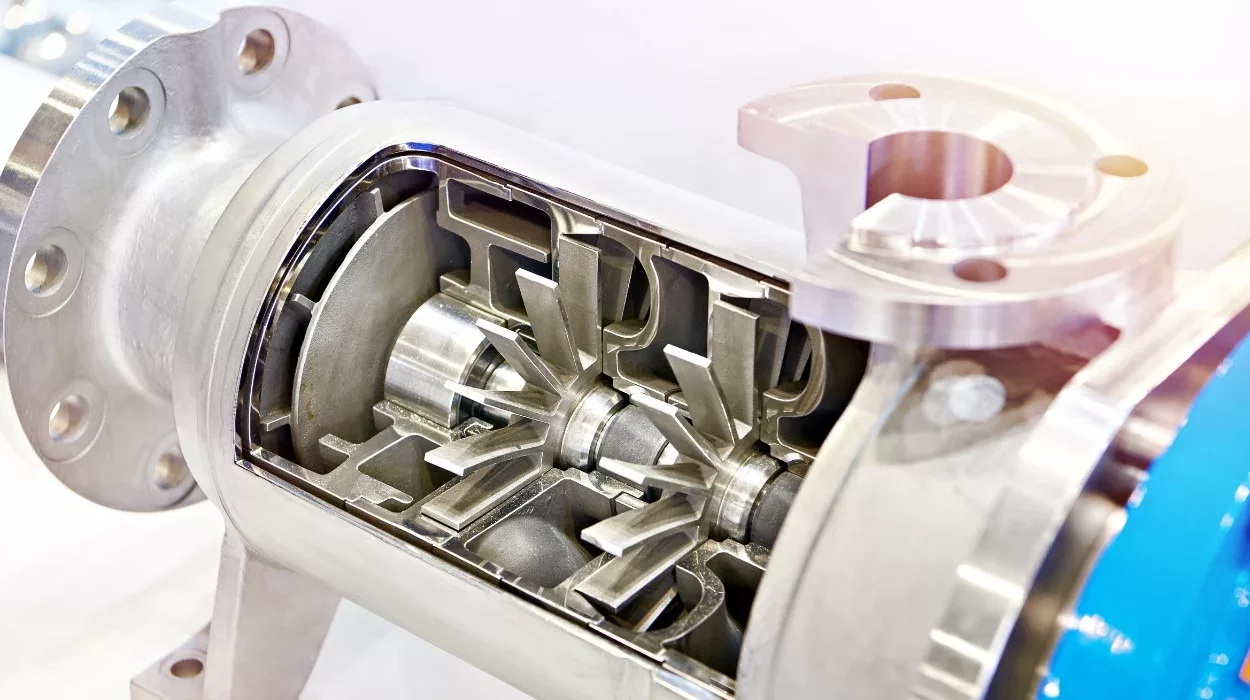
A magnetic drive, called a magnetic coupling, transfers rotational motion and power between two rotating shafts without requiring physical contact. It doesn’t need any maintenance and can bear varying torques. High-quality products free from contamination are guaranteed by specific glass joints (B24, B34, B/NS29/32, and B/NS45/40).
The magnetic drive’s applications demonstrate its diversity and user-friendliness. To utilize it, affix one end to the nozzle of the glass vessel and the other to the stirrer motor. At the bottom is a glass shaft attached to a PTFE impeller. This gadget can withstand the torque from different overhead stirrers and is compatible with glass jars up to 50 liters in capacity. It is constructed of Hastelloy SS316 and runs at up to 3000 RPM.
How does a Magnetic Drive work?
Magnetic drive has two primary parts: the rotor and the stator. The stator, a stationary component, houses electromagnets, which an electric current can turn on and off. On the other hand, the rotor revolves and is made of magnets. A magnetic field is created when the rotor’s magnets interact with the stator electromagnets.
Magnets on the rotor are oriented concerning the magnetic field produced by the stator to provide a force of repulsion or attraction. This force allows the rotor to revolve. Next, the rotor is accurately regulated by managing the electromagnet’s activation and deactivation.
Features of Magnetic Drives:
- Leak-free Operation: Magnetic drive pumps employ sealless technology, eliminating the need for mechanical seals. This implies there won’t be any leaks even when working with caustic chemicals. As a result, maintenance expenses are reduced, and system uptime is increased.
- Run-Dry Capability: The drive’s carbon bushing protects it from harm in run-dry conditions. This feature is invaluable in unsupervised situations.
- Chemical resistance: The magnetic drive pumps significantly improve plant safety for operators and technicians by offering exceptional resistance to strong chemicals. This unique feature guarantees the drive can resist exposure to corrosive substances, offering a dependable and secure option for chemical processing applications.
- Durability: This drive can operate effectively in severe chemicals and extremely high temperatures.
- Minimal Maintenance: Magnetic drives require little maintenance. Magnetic seals are resistant to corrosion and don’t require replacement mechanical seals.
Technical features of magnetic drive:
- Max. Discharge Capacity 5.5 – 135 L/min / 6 – 135 L/min
- Max. Head 1 – 14.3 m / 1.4 – 20.3 m
- Main Materials GFRPP
- Required Power Range 5 – 260 W
- Power Supply AC100V Single phase, 220V – 240V Single phase 220V, 380V, 400V, 440V Three phase
- Liquid Temperature Range 0 – 80°C
- Specific Gravity Limit Up to approx. 1.3 (depending on model)
- Sealing Method Seal-less construction
Applications of Magnetic Drives:
Magnetic drive pumps are helpful in many sectors, mainly when leakage occurs. They are frequently utilized to move fluids in compressors and pumps. Because they don’t have shaft seals, drives are perfect for handling corrosive or dangerous substances. Electric vehicles use magnetic drives to transmit power from the motor to the wheels. Their dependability and efficiency improve electric vehicle performance. In the petrochemical sector, they are also used to transport hazardous and flammable fluids.
How To Use Magnetic Drive Pump
Here are a few handy points to using a magnetic drive pump
- Always prime the pump before the operation to prevent component melting and liquid loss.
- Use clean liquids without suspended solids to avoid obstruction of the closed impeller.
- Ensure proper suction conditions to prevent cavitation, ideally installing the pump under the head.
- Before selecting a pump, calculate system head requirements, including geodetic height and all losses.
- Consider fluid properties like viscosity and density when choosing motor power and calculating head losses.
- Monitor operating temperature as it significantly affects fluid viscosity and pump performance.
- Operating the pump at a cool temperature is recommended to prevent overheating and potential damage to components.
Safety Measures:
Consider the following safety measures to avoid accidents:
- Surplus protection devices can be added to magnetic drives to protect them from harm in the case of an excessive load.
- Magnetic drives can handle corrosive fluids because their materials are resistant to corrosion.
- A simple and trustworthy method exists to stop the drive in an emergency or other pressing circumstance. Emergency stop buttons and remote shutdown alternatives safeguard personnel and equipment.
- The sealed construction ensures no physical connection between the driving components and eliminates fluid leaks.
- Magnetic drives are made to keep external elements and electrical components apart. This guarantees the drive operates securely within predetermined electrical limits and lowers the possibility of electrical shocks.