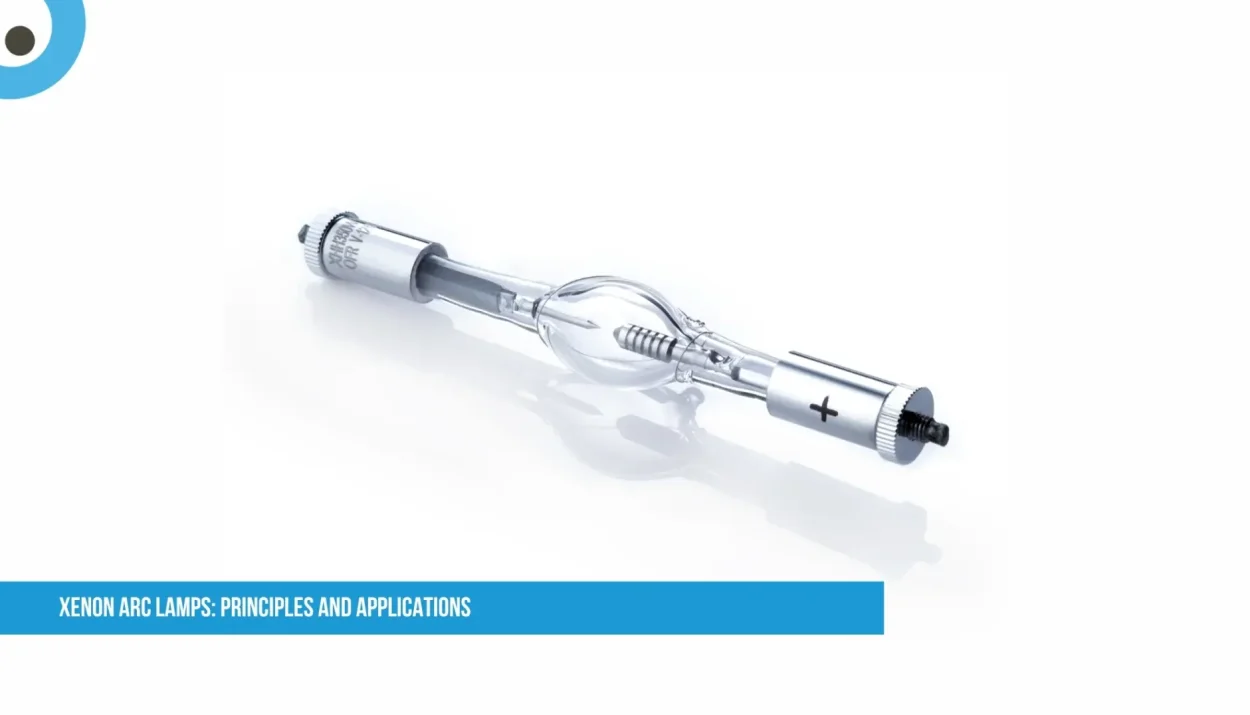
What is a Xenon Arc Lamp?
A xenon arc lamp is a type of high-intensity electric light that produces bright, white light by passing electricity through xenon gas. It works similarly to how lightning flashes in the sky—electricity jumps between two electrodes inside a glass tube filled with xenon gas, creating a bright arc of light.
Key Features: –
- Very bright – Can produce intense light, similar to sunlight.
- Wide color spectrum – Emits light across ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) wavelengths.
- Instant on/off – Unlike some lamps that need warm-up time, xenon lamps light up immediately.
- Long lifespan – Can last hundreds to thousands of hours, depending on usage.
How Does a Xenon Arc Lamp Work?
Electric Arc Creation:
Inside the lamp, two electrodes (positive and negative) are separated by a small gap.
When high voltage is applied, an electric arc forms between them, ionizing the xenon gas.
Light Emission:
The ionized xenon gas emits a bright glow, producing a continuous spectrum of light.
The light is very close to natural sunlight, making it useful for many applications.
Types of Xenon Arc Lamps:
Short-arc lamps (compact, high-intensity, used in projectors and scientific equipment).
Long-arc lamps (used in searchlights and industrial lighting).
Flash lamps (produce quick bursts of light, used in photography and medical devices).
Applications of Xenon Arc Lamps
Because of their brightness and sun-like spectrum, xenon arc lamps are used in:
Cinema Projectors
Used in high-end movie projectors because they provide bright, true-color light.
Solar Simulation
Mimics sunlight for testing solar panels, spacecraft materials, and weather resistance.
Medical & Dermatology
Used in UV therapy, sterilization, and intense pulsed light (IPL) treatments for skin conditions.
Separated by a small gap.
Automotive Headlights
Some high-end cars use xenon HID (High-Intensity Discharge) headlights for better visibility.
Industrial & Scientific Uses
Spectroscopy, microscopy, and material testing due to their stable light output.
Photography & Strobe Lights
Flash photography and high-speed imaging rely on xenon flash lamps.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Xenon Arc Lamps
Advantages:
Extremely Bright Light
Produces intense, high-luminosity light, close to natural sunlight.
Ideal for applications requiring powerful illumination (e.g., projectors, searchlights).
Broad Spectrum Output
Covers ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) wavelengths.
Useful in scientific instruments, solar simulation, and medical treatments.
Instant On/Off (No Warm-Up Time)
Unlike some lamps (e.g., metal halide), xenon lamps reach full brightness immediately.
High Color Rendering Index (CRI ~95-100)
Reproduces colors accurately, making it great for cinema, photography, and medical imaging.
Disadvantages:
High Cost
More expensive than LEDs, halogen, or fluorescent lamps.
High Power Consumption
Requires a lot of electricity, increasing operational costs.
Heat Generation
Produces significant heat, requiring cooling systems (fans/heat sinks).
High-Pressure Risk
Contains pressurized xenon gas, which can be hazardous if the lamp breaks.
Future of Xenon Arc Lamps
While LEDs are becoming more popular due to energy efficiency, xenon lamps still dominate in areas requiring ultra-bright, high-quality light. However, advancements in LED technology may reduce their use in some applications over time.
Conclusion: Xenon arc lamps are powerful light sources with unique benefits, especially where brightness, color accuracy, and reliability matter most.